Koshi Pradesh Fifth Level Health Assistant Loksewa Syllabus: The syllabus of competitive examination for the posts of Health Assistant, Assistant Level Fifth Level, Health Inspection Group, Health Service under the Province Civil Service and Local Government Service is published by the Koshi Pradesh Loksewa Aayog ( Public Service Commission of Koshi Province). This Koshi Pradesh Loksewa syllabus of fifth level Health Assistant from 3rd Falgun of 2080.
Koshi Pradesh Fifth Level Health Assistant Loksewa Syllabus
Source: Koshi Province Public Service Commission
Note:
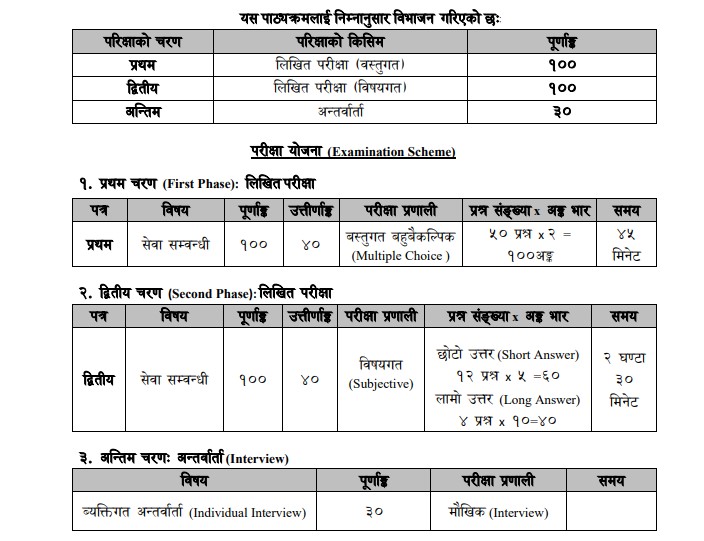
1. This syllabus is divided into three phases:
- Phase I (Written Examination: Subject-Based)
- Phase II (Written Examination: Subject-Based)
- Phase III (Intermediate).
2. The question paper will be in Nepali or English.
3. The medium of the written examination will be Nepali or English or both Nepali and English.
4. In case of incorrect answers to multiple choice questions, 20% marks will be deducted for each incorrect answer. However, if no answer is given, no marks will be given for that and no marks will be deducted.
5. Items such as mobile phones, smart watches, headphones or similar electronic devices, books, notebooks, bags, etc. will not be allowed in the examination hall.
6. In the case of the marks allotted for thematic questions, one long question or two or more parts of a single question or two or more short notes under one question may be asked.
7. The number of questions, marks and weightage given to them in the examination shall be as much as possible as given in the relevant paper/subject.
8. In the case of the second paper (paper having thematic questions), there shall be separate answer sheets for each section. The examinee shall have to write the answers to the questions of each section in the answer sheet of the same section.
9. The number of questions to be asked from the units of the syllabus of the first and second papers shall be as follows:
| First Paper Units | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 |
| No. Questions | 4 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 2 |
| Marks | 8 | 12 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 4 | 8 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 4 |
| Second Paper | Part A | Part B | ||||||||||||||
| Long Answer Question | 2 | 2 | ||||||||||||||
| Short Answer Question | 6 | 6 | ||||||||||||||
| Marks | 50 | 50 | ||||||||||||||
10. Not withstanding anything written in the content of the papers/subjects under this curriculum plan, the laws, acts, rules and policies included in the curriculum that are in force (amended or amended and deleted or amended and added) 3 months before the date of the examination shall be deemed to have been included in this curriculum.
11. Only candidates selected from the written examination of the first phase will be invited to the written examination of the second phase.
12. The result of the written examination will be published on the basis of the total marks obtained in the first phase of the written examination and the marks obtained in the second phase.
13. Only candidates who qualify the written examination will be considered for the final round of selection.
14. The final round of selection will be announced based on the total marks of the written examination and the final round of selection.
First and Second Paper: Service-Related
Part A
1. Anatomy and Physiology
Anatomical structure and function of the following different organs of the body system:
a) Digestive system
b) Respiratory system
c) Cardiovascular system
d) Reproductive system
e) Endocrine system
f) Nervous system
g) Skeletal system
h) Muscular System
i) Urinary System
j) Sense organ system
2. National Policy, Planning, Strategies and implementation status of Public Health Programmes in Nepal
a) Family Planning, Safe Motherhood and Newborn Health, Primary Health Care, and Out Reach Clinic
b) Control of Diarrhoeal Diseases (CDD), Acute Respiratory Diseases (ARI), Nutrition, National Programme on Immunization & Integrated Management of Neonatal and Childhood Illness (IMNCI), COVID 19 and other epidemic management
c) Malaria, Kala-azar, Dengue, Japanese Encephalitis, Filaria, Scrub Typhus, Leptospirosis
d) Human Immuno-deficiency Virus (HIV)/Acquired Immuno-Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS) and Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD) Control
e) Tuberculosis and Leprosy Elimination
f) Health Insurance
g) Health Education, Information, and Communication
h) Nepal Health Sector Strategy
i) Health Sector in SDG
3. Planning and Management
a) Community Health Diagnosis & Health Profile
b) Micro Planning of Health Programmes
c) Supervision, Monitoring, and Evaluation of Health Programmes
d) Integrated Health Management Information System (IHMIS)
e) Planning and Management of Camps
f) Cold Chain Management
g) Health Training Management in different settings
h) Logistic Management and Logistic Management Information System
4. Organizational Structure and Functions
a) Ministry of Health and Population (MoHP), Department of Health Service (DoHS), Provincial Ministry of Health (MoH), Provincial Health Directorate (PHD), Provincial Health Training Centre (PHTC), Provincial Health Logistic Management Center (PHLMC), Provincial Public Health Laboratory (PPHL)
b) Health Office (HO), health organogram of local level, Different levels of provincial and local hospitals
c) Primary Health Care Center (PHCC), Health Post (HP), Basic health service Center, Urban Primary Health Center (UPHC), Community Health Unit
d) Structure of health service in federal context
e) Job description of Health Assistant
5. Community Mobilization & Local Governance
a) Female Community Health Volunteers (FCHV) and Mother’s Groups
b) Primary Health Care Outreach Clinic
c) Mobilization of Local Health Leaders and Committee
d) Federalization in Health Services
6. Epidemiology and Disease Control
a) Definition, Scope, Causes of Disease, and Infection
b) Types and Management of Disasters
c) Management of Epidemics and recent challenges
d) Causes, Signs, Symptoms, Management, Prevention and Control of Gastroenteritis, Dysentery, Cholera, Typhoid Fever, Giardiasis, Malaria, Filariasis, Encephalitis, Kala-azar, Dengue, Parasitic Infestation, Scabies, Chicken Pox, Influenza, Mumps, Rabies, Hepatitis, Ring Worm, Leprosy, Tuberculosis, Helminthiasis, Pertussis, Measles, and Diphtheria
e) Non-communicable Diseases (General Introduction): Heart Diseases, Cancer, Diabetes, Kidney Problems, and Common Mental Health Problems
7. Environmental Sanitation
a) Water Purification,
b) Waste Management,
c) Food Hygiene, Sanitation of public places, Health Hazards,
d) Sanitary Latrines,
e) Basic Measures in Controlling Rodents,
f) Integrated Vector Management,
g) Medical Importance, and Measures of Controlling Common Vectors and Insects
8. Child Health Problems and Interventions
a) Common Neo-natal Health Problems
b) Common Child Health Problems like CDD, ARI, Malaria, and Malnutrition
c) Nutritional Interventions (Management of SAM/MAM cases), Immunizations Services
Part B
9. General Medicine
a) General History Taking, Simple Physical Examination, Systemic Examination
b) Various Methods of Diagnosis, Complications and Management of Diseases in Respiratory, Digestive, Cardiovascular, Urinary, Endocrine, Hematology, and Central Nervous System with their terminology, Etiology and clinical features
10.First Aid and Emergency Management
Basic Life Support (BLS), Shock, Poisoning, Injuries, Haemorrhage, External bleeding, Thermal and Chemical Burns, Fracture and Dislocation, Frost Bite, Insect bite, Animal bite, Snake bite and Drowning, Abscess and cellulitis
11.Skin Diseases
Impetigo, Contagious, Boils, Tinea Infection, Herpes Zoster, Scabies, Eczema, Allergic Conditions, and Acute drug reaction
12.Elementary Surgery
Hemorrhoids, Management of inflammation, Septicemia, Toxemia, Sinus, fistula, Gangrene, Wound, Tetanus, Acute Pain Abdomen, Hernia, Anal Fissure, Acute Retention of Urine, Causes of Frequent Urination and Nocturia, Management of Rupture of Urethra, Haematuria, Phimosis, Para phimosis, Hydrocele, Head Injury, Clinical features and management of Osteomyelitis, Local Anesthesia, Sterilization of Surgical Instruments
13.Eye, Ear, Nose and Throat Diseases
a) General Examination procedures of Eye, Ear, Nose, and Throat
b) Sign and Symptoms and General Management of Eye Lid Complications, Red Eyes, Trachoma, Corneal ulcer, Night Blindness, Cataract, Pterygium, Iridocyclitis, Glaucoma, and foreign body in the eyes
c) Removal of Wax and Foreign Bodies, Signs and Symptoms, and Management of Otitis Media, Otitis Externa, and referral conditions of hearing problems
d) Deviated nasal Septum, Nasal polyps, Epistaxis and Sinusitis
e) Clinical Features, Complications, and Management of Acute Tonsillitis, Pharyngitis, and Laryngitis
14.Oral Health and Mental Health
a) Dental plaques and calculus, Dental Carries, Periodontitis, Periodontal pockets and Abscess, Importance and Maintenance of Oral Hygiene
b) Psychosis, Neurosis and Mental Retardation
15.Reproductive Health Problems and Interventions
a) Male and Female Reproductive System, Menstruation Cycle, Conception, ovulation, Vaginal Discharge, Management of Per Vaginal Bleeding, Post-menopausal Bleeding, Uterine Prolapsed, Pelvic Inflammatory Diseases; causes, Sign, Symptoms, and Complications of Ectopic pregnancy, Management of Mastitis and Breast Abscess
b) Normal Labor and Early Diagnosis and referral of Complicated Pregnancy, Puerperium
c) Safe Abortions
d) Family Planning and Counselling, Permanent and Temporary Contraceptives
16.Acts and Regulations
a) Rights and policies related to health in The Constitution of Nepal
b) Public Health Service Act 2075 and Public Health Service Regulation 2077
c) Koshi Province Public Health Act 2074
d) Local government operation Act 2074
e) Public Procurement Act 2063 and Regulations
f) The Prevention of Corruption Act 2059
g) Right to Information Act, 2064 (2007)
h) Provincial good governance (Management and Operation) Act, 2076 and Regulation 2079
i) Health Professional Council Act and Regulation
j) Civil service act (Province and local level)
Model Questions (Multiple Choice Questions)
1. The most sensitive indicator for the health status of the country is:
a. IMR
b. CDR
c. MMR
d. TFR
2. The most common treatment for vibrio cholera is:
a. Vaccine
b. Oral rehydration
c. Surgery
d. Antibiotics
3. The first dose of Measles-Rubella (MR) is given at …… months as per National Immunization
Schedule.
a. 9 months
b. 10 months
c. 12 months
d. 15 months.
4. Vaginal examination is contraindicated in:
a. Incomplete abortion
b. Placenta previa
c. Cervical erosion
d. Multiple pregnancy
5. The target group for Vitamin supplementation program is:
a. 0-6 months.
b. 6months- 59 months.
c. 1 year – 3 years
d. 0- 5 year
Model Questions (Subjective)
1. Define Malaria with its Cardinal Signs and Symptoms. How do you treat an adult case of Plasmodium vivax malaria in the Health Post Level? (5+5=10)
2. List out the major Nutritional Problems in Nepal. What are the roles of Health Assistant in Nutritional intervention programs? (2+ 3=5)
3. Define Shock? Briefly describe its first aid and emergency management in Health Post level? (1 + 4=5)
Find the Loksewa Syllabus of Other Job Positions at Nitesh’s Blog Loksewa Curriculum/Syllabus section.

