Health Assistant LokSewa Syllabus of Gandaki Province
The syllabus is specifically designed for Nepal Health Service, Health Inspection Group, fifth level Health Assistant Open and Internal written competitive exam of Gandaki Province. The syllabus is designed for both Provincial level as well as Local level written competitive exam of Gandaki Province.
The syllabus is designed for both Provincial level as well as Local level written competitive exam of Gandaki Province.
Nepal Health Service, Health Inspection Group, Fifth Level, Health Assistant (Province and Local Level) Open and Internal Written Competitive Exam Syllabus
The LokSewa examination for the post of fifth level Health Assistant will be help in two phases as per the Health Assistant LokSewa syllabus of Gandaki Province.- First Phase: Written Examination.
- First Paper: Full Marks: 100
- Second Paper: Full Marks: 100
- Second Phase: Interview
- Full Marks: 30
First Phase: Written Examination Scheme
First Paper Written Examination:- Subject: General Knowledge & General Mental Ability Test and Job Based Knowledge
- Full Marks: 100
- Pass Marks: 40
- Examination System: Objective Questions [Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)]
- Number of Questions: 50; each Question consisting 2 Marks [50×2=100] (25 MCQs from General Knowledge & General Mental Ability Test and 25 MCQs from Job Based Knowledge)
- Time: 45 minutes
- Subject: Job Based Knowledge
- Full Marks: 100
- Pass Marks: 40
- Examination System: Subjective Questions [Short Answer and Long Answer]
- Number of Questions: 16; 12 Short answers (12×5=60 Marks) and 4 Long answers (4×10=40 Marks)
- Time: 2 hours 15 minutes
Second Phase Examination: Interview
- Subject: Interview
- Full Marks: 30
- Examination System: Board Interview
Gandaki Province H.A. First Paper Written Examination Syllabus: (Objective Questions)
- Part 1 of First Paper:
- Section 1: General Awareness: 30 Marks (15×2=30 Marks)
- Section 2: General Aptitude Test: 20 Marks (10×2=20 Marks)
- Part 2 of First Paper:
- Job Based Knowledge: 50 Marks (25×2=50 Marks)
H.A. Loksewa Syllabus: First Paper – Part 1 General Awareness and General Aptitude Test
- Section A: [15 Que. x 2 Marks=30 Marks]
- 1. General Knowledge/Awareness: 16 Marks
- 2. Public Management: 14 Marks
- Section B: [10 Que. x 2 Marks=20 Marks]
- 3. General Aptitude Test: 20 Marks

H.A. Loksewa Syllabus: First Paper – Part 2
-
- The examination may be conducted in Nepali or English language or both English and Nepali language.
- The number of questions from each chapter of the curriculum/syllabus will be asked as mentioned below.
| Unit | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| No. of Questions | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
1 |
-
- For each right answer, 2 marks will be provided and, 20% marks will be deducted in case of the wrong answer. No marks will be given or deducted if the question is unanswered.
- Only the selected candidates from the first phase of examination will be called for interview in the second phase of the examination.
1.Introduction of Health Policy, Planning, Strategies and implementation status of Public Health Programs in Nepal
1.1 Family Planning, Safe Motherhood, Reproductive Health1.2 Control of Diarrhoeal Diseases (CDD), Acute Respiratory Diseases (ARI), Nutrition, National Program on Immunization & Integrated Management of Childhood Illness (IMCI) 1.3 Malaria, Kala-azar, Japanese Encephalitis, Filaria 1.4 Human Immuno-Deficiency Virus (HIV)/Acquired Immuno-Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS) and Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD) Control 1.5 Tuberculosis and Leprosy Control 1.6 Health Education, Information and communication2. Planning and Management
2.1 Community Health Diagnosis & Health Profile 2.2 Micro Planning of Health Program 2.3 Supervision, Monitoring and Evaluation of Health Programs 2.4 Health Management Information System (HMIS) 2.5 Planning and Management of Camps 2.6 Cold Chain Management 2.7 Health Training Management in different settings 2.8 Logistic Management3. Organizational Structure and Functions
3.1 Federal Level: Ministry of Health and Population (MoHP), DoHS and Central Level agencies/Hospitals 3.2 Provincial Level: Ministry of Health and Population, Health Directorate, Health Logistics Management Center, Health Training Center and Public Health Lab of Gandaki Province, Health Offices (HO) and Provincial Hospitals 3.3 Local Level: Primary Hospitals, Primary Health Care Center (PHCC), Health Post (HP), Urban Health Center, Basic Health Center4. Community Mobilization & Local Governance
4.1 Female Community Health volunteers (FCHV) and Mother’s Groups 4.2 Primary Health Care Outreach Clinic 4.3 Community Drug Program (CDP) 4.4 Mobilization of Local Health Leaders and Committees5. Epidemiology and Disease Control
5.1 Definition, Scope, Causes of Disease and Infection 5.2 Types and Management of Disasters 5.3 Management of Epidemics 5.4 Causes, Signs, Symptoms, Management, Prevention and Control of Gastroenteritis, Dysentery, Cholera, Typhoid Fever, Giardiasis, Malaria, Filariasis, Encephalitis, Kala-azar, Parasitic Infestation, Scabies, Chicken Pox, Influenza, Mumps, Rabies, Hepatitis, Ring Worm, Leprosy, Tuberculosis, Helminthiasis, Pertussis, Measles and Diphtheria,COVID-19,Monkeypox, Typhus fever ,Brucellosis, Leptospirosis, Dengue fever, DHF,DSS6. Environmental Sanitation
6.1 Water Purification, Waste Management, Food Hygiene, Sanitation of public places, Health Hazards, Sanitary Latrines, Basic Measures in Controlling Rodents, Medical Importance and Measures of Controlling Common Vectors and Insects7. Child Health Problems and Interventions
7.1 Common Neo-natal Problems 7.2 Common Child Health Problems like CDD, ARI, Malaria and Malnutrition 7.3 Nutritional Interventions, Immunizations Services8. General Medicine
8.1 General History Taking, Simple Physical Examination, Systemic Examination 8.2 Various Methods of Diagnosis, Complication and Management of Diseases in Respiratory, Digestive, Cardiovascular, Urinary, Endocrine, Hematology and Central Nervous System with its terminology, Etiology and clinical features9. First Aid and Emergency Management
9.1 Shock, Poisoning, Injuries, Haemorrhage, External bleeding, Thermal and Chemical Burns, Fracture and Dislocation, Frost Bite, Heat stroke, Insect bite, Animal bite, Snake bite and Drowning, Abscess and Cellulites, 9.2 Primary Trauma Care, Disaster Management and Triaging 9.3 Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (BLS and ACLS)10. Skin Diseases
10.1 Impetigo, Contagious, Boils, Tinea Infection, Herpes Zoster, Scabies, Eczema, Allergic Conditions and Acute drug reaction11. Elementary Surgery
11.1 Hemorrhage, Management of inflammation, Septicemia, Toxemia, Sinus, fistula,Gangrene, Wound, Tetanus, Acute Pain Abdomen, , Hernia, Anal Fissure, Piles, Acute Retention of Urine, Causes of Frequent Urination and Nocturia, Management of Rupture of Urethra, Hematuria, Phimosis, Paraphimosis, Hydrocele, Head Injury, Clinical features and management of Osteomyelitis, Local Anesthesia, Sterilization of Surgical Instruments12. Eye, Ear, Nose and Throat Diseases
12.1 Eye: General Examination procedures of Eye, Sign and Symptoms and General Managements of Eye Lid complications, Red Eyes, Trachoma, Corneal ulcer, Night Blindness, Cataract, Pterygium, Iridocyclitis, Glaucoma and foreign body in the eyes 12.2 Ear: General Examination procedures of Ear, Removal of Wax and Foreign Bodies, Sign and Symptoms and Managements of Otitis Media, Otitis Externa and referral conditions of hearing problems 12.3 Nose: General Examination procedures of Nose, Deviated nasal Septum, Nasal polyps, Epistaxis and Sinusitis 12.4 Throat: General Examination procedures of Throat, Clinical Features, Complications and management of Acute Tonsillitis, Pharyngitis and Laryngitis13. Oral Health and Mental Health
13.1 Oral Health: Dental plaques and calculus, Dental Carries, Periodontitis, Periodontal pockets and Abscess, Importance and Maintenance of Oral Hygiene 13.2 Mental Health: Psychosis, Neurosis and Mental Retardation15. Reproductive Health Problems and Interventions
14.1 Male and Female reproductive System, mechanism of Menstruation, Conception, Evolution, Vaginal Discharge, Management of Per Vaginal Bleeding, Post Menopausal Bleeding, Uterine Prolapsed, Pelvic Inflammatory Diseases; causes, Sign, Symptoms and Complication of Entopic pregnancy, Management of Engorgement of Mastitis. and Breast Abscess 14.2 Management of Normal Labor and Early Diagnosis and referral of Complicated Pregnancy, Labor, Puerperium 14.3 Safe Abortions, Medical method of Abortion, Permanent and Temporary Contraceptives15. Acts and Regulations
15.1 Current Health Policy (National and Gandaki Province) 15.2 Health Service Act 2053 and Regulation 2055 15.3 Health Professional Council Act 2053 and Regulation 2056 15.4 Local government operation act 2074 section 1-4 and 11 15.5 Health Insurance act 2074 15.6. Public Health Service Act, 2075 and Public Health Service Rule and Regulation 2077Gandaki Province H.A. Second Paper Written Examination Syllabus: (Subjective Questions) – Job Based Knowledge
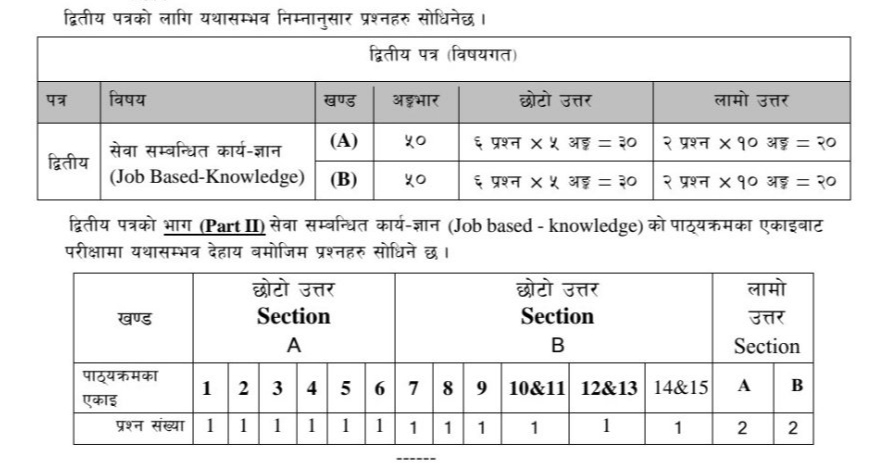
SECTION A: 50 MARKS
1. Introduction, National Policy, Planning, Strategies and implementation status of Public Health Programs in Nepal
1.1 Family Planning, Safe Motherhood, Reproductive Health 1.2 Control of Diarrhoeal Diseases (CDD), Acute Respiratory Diseases (ARI), Nutrition, National Program on Immunization & Integrated Management of Childhood Illness (IMCI) 1.3 Malaria, Kala-azar, Japanese Encephalitis, Filaria 1.4 Human Immuno Deficiency Virus (HIV)/Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS) and Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD) Control 1.5 Tuberculosis and Leprosy Control 1.6 Health Education, Information and communication2. Planning and Management
2.1 Community Health Diagnosis & Health Profile 2.2 Micro Planning of Health Program 2.3 Supervision, Monitoring and Evaluation of Health Programm 2.4 Health Management Information System (HMIS) 2.5 Planning and Management of Camps 2.6 Cold Chain Management 2.7 Health Training Management in different settings 2.8 Logistic Management3. Organizational Structure and Functions
3.1 Federal Level: Ministry of Health and Population (MoHP), DoHS and Central Level agencies/Hospitals 3.2 Provincial Level: Ministry of Health and Population, Health Directorate, Health Logistics Management Center, Health Training Center and Public Health Lab of Gandaki Province, Health Offices (HO) and Provincial Hospitals 3.3 Local Level: Primary Hospitals, Primary Health Care Center (PHCC), Health Post (HP), Urban Health Center, Basic Health Center4. Community Mobilization & Local Governance
4.1 Female Community Health volunteers (FCHV) and Mother’s Groups 4.2 Primary Health Care Outreach Clinic 4.3 Community Drug Program (CDP) 4.4 Mobilization of Local Health Leaders and Committees5. Epidemiology and Disease Control
5.1 Definition, Scope, Causes of Disease and Infection 5.2 Types and Management of Disasters 5.3 Management of Epidemics 5.4 Causes, Signs, Symptoms, Management, Prevention and Control of Gastroenteritis, Dysentery, Cholera, Typhoid Fever, Giardiasis, Malaria, Filariasis, Encephalitis, Kala-azar, Parasitic Infestation, Scabies, Chicken Pox, Influenza, Mumps, Rabies, Hepatitis, Ring Worm, Leprosy, Tuberculosis, Helminthiasis, Pertussis, Measles and Diphtheria,COVID-19,Monkeypox, Typhus fever ,Brucellosis, Leptospirosis, Dengue fever, DHF,DSS6. Environmental Sanitation
6.1 Water Purification, Waste Management, Food Hygiene, Sanitation of public places, Health Hazards, Sanitary Latrines, Basic Measures in Controlling Rodents, Medical Importance and Measures of Controlling Common Vectors and InsectsSECTION B: 50 MARKS
7. Child Health Problems and Interventions
7.1 Common Neo-natal Problems 7.2 Common Child Health Problems like CDD, ARI, Malaria and Malnutrition 7.3 Nutritional Interventions, Immunizations Services8. General Medicine
8.1 General History Taking, Simple Physical Examination, Systemic Examination 8.2 Various Methods of Diagnosis, Complication and Management of Diseases in Respiratory, Digestive, Cardiovascular, Urinary, Endocrine, Hematology and Central Nervous System with its terminology, Etiology and clinical features9. First Aid and Emergency Management
9.1 Shock, Poisoning, Injuries, Haemorrhage, External bleeding, Thermal and Chemical Burns, Fracture and Dislocation, Frost Bite, Heat stroke, Insect bite, Animal bite, Snake bite and Drowning, Abscess and Cellulites, 9.2 Primary Trauma Care, Disaster Management and Triaging 9.3 Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (BLS and ACLS)10. Skin Diseases
10.1 Impetigo, Contagious, Boils, Tinea Infection, Herpes Zoster, Scabies, Eczema, Allergic Conditions and Acute drug reaction11. Elementary Surgery
11.1 Hemorrhage, Management of inflammation, Septicemia, Toxemia, Sinus, fistula, Gangrene, Wound, Tetanus, Acute Pain Abdomen, , Hernia, Anal Fissure, Piles, Acute Retention of Urine, Causes of Frequent Urination and Nocturia, Management of Rupture of Urethra, Hematuria, Phimosis, Paraphimosis, Hydrocele, Head Injury, Clinical features and management of Osteomyelitis, Local Anesthesia, Sterilization of Surgical Instruments12. Eye, Ear, Nose and Throat Diseases
12.1 Eye: General Examination procedures of Eye, Sign and Symptoms and General Managements of Eye Lid complications, Red Eyes, Trachoma, Corneal ulcer, Night Blindness, Cataract, Pterygium, Iridocyclitis, Glaucoma and foreign body in the eyes 12.2 Ear: General Examination procedures of Ear, Removal of Wax and Foreign Bodies, Sign and Symptoms and Managements of Otitis Media, Otitis Externa and referral conditions of hearing problems 12.3 Nose: General Examination procedures of Nose, Deviated nasal Septum, Nasal polyps, Epistaxis and Sinusitis 12.4 Throat: General Examination procedures of Throat, Clinical Features, Complications and management of Acute Tonsillitis, Pharyngitis and Laryngitis13. Oral Health and Mental Health
13.1 Oral Health: Dental plaques and calculus, Dental Carries, Periodontitis, Periodontal pockets and Abscess, Importance and Maintenance of Oral Hygiene 13.2 Mental Health: Psychosis, Neurosis and Mental Retardation14. Reproductive Health Problems and Interventions
14.1 Male and Female reproductive System, mechanism of Menstruation, Conception, Evolution, Vaginal Discharge, Management of Per Vaginal Bleeding, Post Menopausal Bleeding, Uterine Prolapsed, Pelvic Inflammatory Diseases; causes, Sign, Symptoms and Complication of Entopic pregnancy, Management of Engorgement of Mastitis. and Breast Abscess 14.2 Management of Normal Labor and Early Diagnosis and referral of Complicated Pregnancy, Labor, Puerperium 14.3 Safe Abortions, Medical method of Abortion, Permanent and Temporary Contraceptives15. Acts and Regulations
15.1 Current Health Policy (National and Gandaki Province) 15.2 Health Service Act 2053 and Regulation 2055 15.3 Health Professional Council Act 2053 and Regulation 2056 15.4 Local government operation act 2074 section 1-4 and 11 15.5 Health Insurance act 2074 15.6. Public Health Service Act, 2075 and Public Health Service Rule and Regulation 2077 You can also check Bagmati Province HA LokSewa syllabus from the link below:Bagmati Province HA LokSewa Syllabus
Sample Questions
1. The route of infection in diarrhea is: (A) Oral to faecal (B) Faecal to Oral (C) Inhalation (D) Skin Contact Correct Answer:- (B) 2. The main objectives of Safer Motherhood is (A) Safe delivery without disturbing the life of mother (B) Safe delivery without disturbing the life of baby (C) A and B (D) None of the above Correct Answer:- (C) 3. Which one does not give guarantee for contraception? (A) Vasectomy (B) Intrauterine Device (C) Oral Pills (D) Breast Feeding Correct Answer:- (D) 4. The elimination of Leprosy means: (A) One case per ten thousand populations. (B) Below one case per ten thousand populations. (C) One case per thousand populations. (D) No one case per ten thousand populations. Correct Answer:- (B) 5. The most sensitive indicator for health status of the country is: (A) IMR (B) CDR (C) MMR (D) TFR Correct Answer:- (A) 6. Coliform present in the water indicates: (A) Excreta contamination in the water (B) Mud in the water (C) Chemical contamination in the water (D) Pure water Correct Answer:- (A)Details of abbreviation used in this curriculum:
- ARI: Acute Respiratory Infection
- AIDS: Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome
- CDR: Crude Death Rate
- CDD: Control of Diarrhoeal Disease
- DHO: District Health Office
- DPHO: District Public Health Office
- DoHS: Department of Health Service
- EPI: Expanded Programme on Immunization
- HIV: Human Immunodefiency Virus
- IMR: Infant Mortality Rate
- IEC: Information, Education and Communication
- HP: Health Post
- SHP: Sub Health Post
- HMIS: Health management Information System
- FP: Family Planning
- FCHV: Female Community Health Volunteers
- TBA: Trained Birth Attendants
- MoHP: Ministry of Health and Population
- RHD: Regional Health Directorate
- MMR: Maternal Mortality Rate
- TFR: Total Fertility Rate
- IMCI: Integrated Management of Childhood illness.


